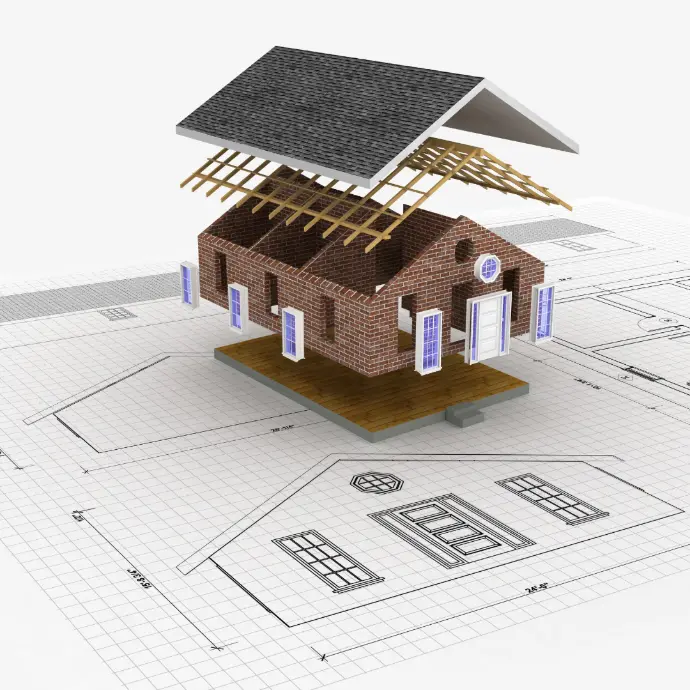
In an era of ever-growing digitalization, the construction industry faces the challenge of increasing efficiency and accuracy in every project stage. 3D modeling has become an important tool in assisting construction project planning, design, and implementation. The two main approaches that are often used in 3D modeling are parametric modeling And direct modeling. Understanding the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of each method is the first step to determining the approach that best suits a project's specific needs.
Parametric Modeling
Parametric modeling is a parameter-based design method. In this approach, model elements are governed by certain rules or parameters such as dimensions, angles, and geometric relationships. The model is automatically updated to reflect the change whenever a parameter value is changed. This process allows the design to be more dynamic, flexible, and structured.
Advantages of Parametric Modeling
Design Flexibility
With parametric modeling, designers can easily change parameter values to customize the design without manually redrawing it. This provides great flexibility, especially in projects with frequently changing design requirements.
Consistency
Any parameter changes are applied automatically across the model, ensuring there are no inconsistencies in the design. This is especially important in large projects involving many parties and disciplines.
Integration with BIM
Parametric modeling is well suited for integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM). With this approach, design data can be used for various purposes such as structural analysis, energy simulation, or cost estimation.
Analysis and Optimization Capabilities
Parametric models enable simulation and analysis, such as structural simulation or cost analysis, so that design decisions can be optimized from an early stage.
Disadvantages of Parametric Modeling

Learning Curve
Parametric modeling requires a deep understanding of the software used and parameter-based design concepts. This may be a challenge for inexperienced users.
Initial Setup Time
To establish parameters and relationships between components in a model, significant time and effort are required, especially in the early stages of a project.

Process Complexity
In some cases, parametric modeling can be too complicated, especially if it is not planned well from the start.
Direct Modeling
Direct modeling, on the other hand, offers a simpler approach. In this method, designers can manipulate the model geometry directly without depending on specific parameters. Direct modeling is often used in the conceptual stage where the exploration of ideas is a top priority.
Advantages of Direct Modeling
Ease of Use
This method is more intuitive and easy to understand, making it suitable for beginners or designers who are not familiar with parametric systems.

Speed in Initial Design
Direct modeling allows designers to create and modify models quickly without having to set parameters. This is very helpful in exploring various design concepts in a short time.

Creative Flexibility
Because they are not bound by parameters, designers have the freedom to experiment with various shapes and ideas without technical limitations.
Disadvantages of Direct Modeling

Lack of Consistency
Because changes are made manually, there is a risk of inconsistency in the design, especially in projects that are complex and involve many parties.

Difficult to Complex Modifications
For design changes that require repeated or large-scale modifications, direct modeling is less efficient than parametric methods.

Limited Integration with BIM
Direct modeling is not designed to support full integration with BIM, so its use in projects that require cross-disciplinary collaboration is limited.
Method Selection in Construction and BIM
The choice between parametric and direct modeling in construction should be based on the specific needs of the project. Here are some guides that may help:
Use Parametric Modeling If:
- Projects require high consistency across models.
- Deep integration with BIM is required for cross-disciplinary collaboration.
- Analysis and simulation are an important part of the design process.
Use Direct Modeling If:
- The project is in an early conceptual stage where exploration of form is a priority.
- The design process requires speed and ease of experimentation.
- The model does not require full integration with BIM.
Integration of Parametric Modeling in BIM
One of the main advantages of parametric modeling is its ability to support BIM processes. In BIM, parametric models can be used to:
- Conflict Detection (Clash Detection). The system automatically detects conflicts between design elements, such as collisions between structures and mechanical installations. This helps prevent problems in the field that can increase project costs and time.
- Scheduling and Cost Estimation (4D and 5D BIM). With parametric data, construction schedules (4D) and cost estimates (5D) can be generated automatically and accurately, providing more transparency in project planning.
- Facilities Management (6D BIM). Parametric data can also be utilized for building operational management after construction is complete, including maintenance and energy management.
Case Studies and Applications
Several large construction projects have proven the benefits of parametric modeling. For example, in skyscraper design, parametric modeling allows structural calculations and wind load simulations with high precision. Additionally, software such as Autodesk Revit or Rhino/Grasshopper has become standard in the industry to support this process.
Conclusion
Parametric and direct modeling are two approaches that have their respective advantages and disadvantages. In the context of construction and BIM, parametric modeling offers greater flexibility, consistency, and integration, while direct modeling excels in ease of use and speed in initial design. The selection of the appropriate method should be based on the specific needs of the project, the complexity of the design, and the level of integration with BIM.
With a deep understanding of these two methods, professionals in the construction industry can make better decisions to optimize the results of their projects.